Raspberry Pi Pico and Pico W
The family
Edit this on GitHub
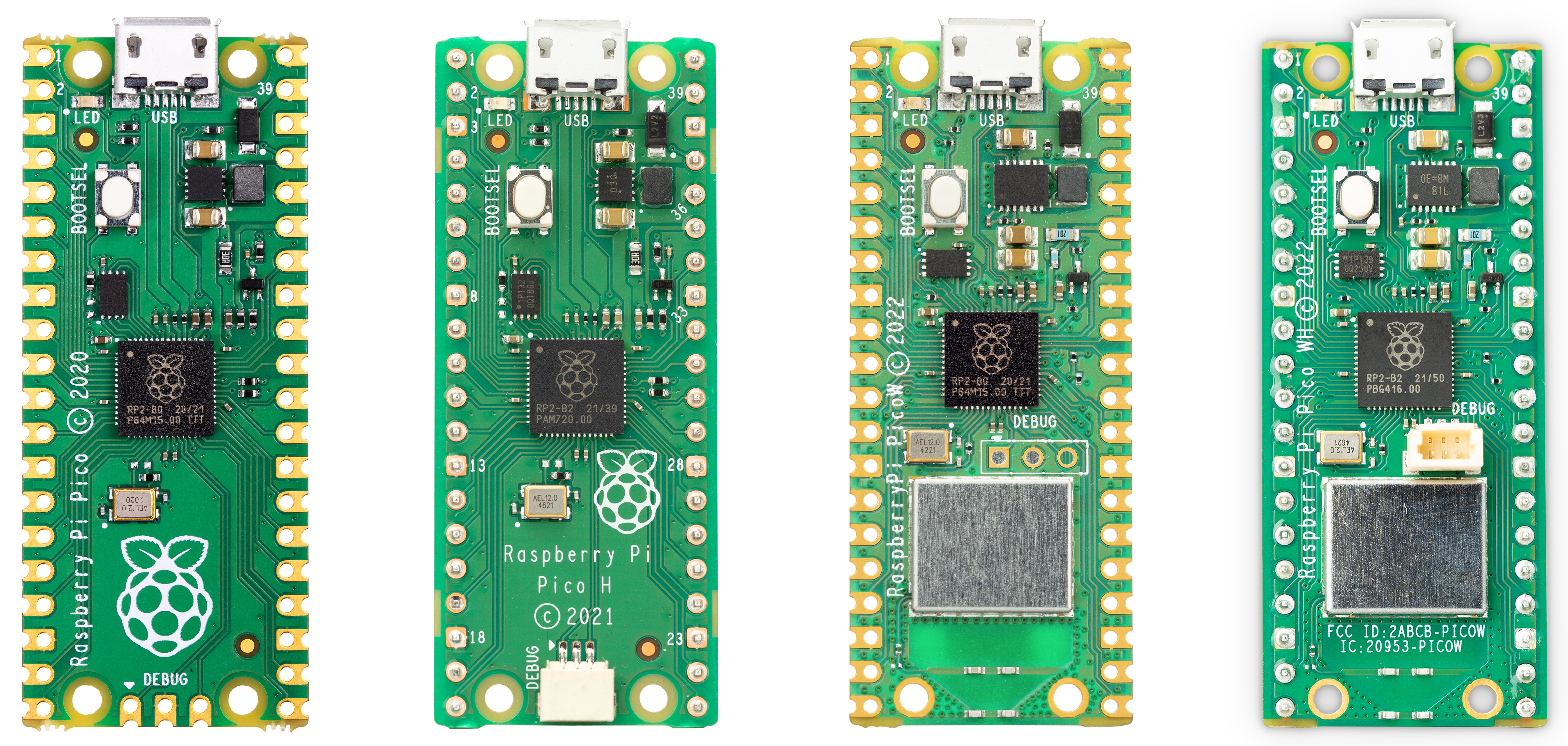
The Raspberry Pi Pico family currently consists of four boards; Raspberry Pi Pico (far left), Pico H (middle left), Pico W (middle right), and Pico WH (far right).
Raspberry Pi Pico and Pico H
Raspberry Pi Pico is a low-cost, high-performance microcontroller board with flexible digital interfaces. Key features include:
-
RP2040 microcontroller chip designed by Raspberry Pi in the United Kingdom
-
Dual-core Arm Cortex M0+ processor, flexible clock running up to 133 MHz
-
264kB of SRAM, and 2MB of on-board flash memory
-
USB 1.1 with device and host support
-
Low-power sleep and dormant modes
-
Drag-and-drop programming using mass storage over USB
-
26 × multi-function GPIO pins
-
2 × SPI, 2 × I2C, 2 × UART, 3 × 12-bit ADC, 16 × controllable PWM channels
-
Accurate clock and timer on-chip
-
Temperature sensor
-
Accelerated floating-point libraries on-chip
-
8 × Programmable I/O (PIO) state machines for custom peripheral support
The Raspberry Pi Pico comes as a castellated module allows soldering direct to carrier boards, while the Pico H comes with pre-soldered headers.
|
Note
|
Both boards have a three pin Serial Wire Debug (SWD) header. However, the Pico H has this broken out into a small, keyed, 3-pin connector while the Pico has three castellated through-hole pins adjacent to the edge of the board. |
Pinout and design files
-
Download the Pinout Diagram (PDF)
-
Download Design Files (Cadence Allegro)
-
Download STEP File
-
Download Fritzing Part for Raspberry Pi Pico
-
Download Fritzing Part for Raspberry Pi Pico H
|
Note
|
More information on Fritzing is available on the fritzing.org website. |
Raspberry Pi Pico W and Pico WH
Raspberry Pi Pico W adds on-board single-band 2.4GHz wireless interfaces (802.11n) using the Infineon CYW43439 while retaining the Pico form factor. The on-board 2.4GHz wireless interface has the following features:
-
Wireless (802.11n), single-band (2.4 GHz)
-
WPA3
-
Soft access point supporting up to four clients
The antenna is an onboard antenna licensed from ABRACON (formerly ProAnt). The wireless interface is connected via SPI to the RP2040 microcontroller.
Due to pin limitations, some of the wireless interface pins are shared. The CLK is shared with VSYS monitor, so only when there isn’t an SPI transaction in progress can VSYS be read via the ADC. The Infineon CYW43439 DIN/DOUT and IRQ all share one pin on the RP2040. Only when an SPI transaction isn’t in progress is it suitable to check for IRQs. The interface typically runs at 33MHz.
For best wireless performance, the antenna should be in free space. For instance, putting metal under or close by the antenna can reduce its performance both in terms of gain and bandwidth. Adding grounded metal to the sides of the antenna can improve the antenna’s bandwidth.
|
Note
|
The CYW43439 wireless chip is connected via SPI to the RP2040. While the CYW43439 supports both 802.11 wireless and Bluetooth, initially Pico W does not have Bluetooth support. Support may be added later, and will use the same SPI interface. If support is added existing hardware may require a firmware update to support Bluetooth, but there will be no hardware modifications needed. |
Pinout and design files
-
Download the Pinout Diagram (PDF)
-
Download Design Files (Cadence Allegro)
-
Download STEP File
-
Download Fritzing Part for Rapsberry Pi Pico W
Documentation
Edit this on GitHub
Documentation for Raspberry Pi Pico and other RP2040-based boards.
RP2040 Device
- RP2040 Datasheet
-
A microcontroller by Raspberry Pi
- Hardware design with RP2040
-
Using RP2040 microcontrollers to build boards and products
Raspberry Pi Pico
- Raspberry Pi Pico Datasheet
-
An RP2040-based microcontroller board
- Getting started with Raspberry Pi Pico
-
C/C++ development with Raspberry Pi Pico and other RP2040-based microcontroller boards
Raspberry Pi Pico W
- Raspberry Pi Pico W Datasheet
-
An RP2040-based microcontroller board with wireless
- Connecting to the Internet with Raspberry Pi Pico W
-
Getting Raspberry Pi Pico W online with C/C++ or MicroPython
Software Development
- Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ SDK
-
Libraries and tools for C/C++ development on RP2040 microcontrollers
- Raspberry Pi Pico Python SDK
-
A MicroPython environment for RP2040 microcontrollers
The API level Doxygen documentation for the Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ SDK is also available as a micro-site.
|
Note
|
A one-click installer for the Pico C/C++ SDK for Windows 10 and Windows 11 is available. |
Software Utilities
Edit this on GitHub
What is on your Pico?
If you have forgotten what has been programmed into your Raspberry Pi Pico, and the program was built using our Pico C/C++ SDK, it will usually have a name and other useful information embedded into the binary. You can use the Picotool command line utility to find out these details. Full instructions on how to use Picotool to do this are available in our 'getting started' documentation.
-
Go to the Picotool Github repository.
Debugging using another Raspberry Pi Pico
It is possible to use one Raspberry Pi Pico to debug another Pico. This is possible via picoprobe, an application that allows a Pico to act as a USB → SWD and UART converter. This makes it easy to use a Pico on non-Raspberry Pi platforms such as Windows, Mac, and Linux computers where you don’t have GPIOs to connect directly to your Pico. Full instructions on how to use Picoprobe to do this are available in our 'getting started' documentation.
-
Download the UF2 file
-
Go to the Picoprobe Github repository
Resetting Flash memory
Pico’s BOOTSEL mode lives in read-only memory inside the RP2040 chip, and can’t be overwritten accidentally. No matter what, if you hold down the BOOTSEL button when you plug in your Pico, it will appear as a drive onto which you can drag a new UF2 file. There is no way to brick the board through software. However, there are some circumstances where you might want to make sure your Flash memory is empty. You can do this by dragging and dropping a special UF2 binary onto your Pico when it is in mass storage mode.
-
Download the UF2 file
-
See the code on Github